
Introduction to AC Circuits and Sine Waves
Overview of AC vs DC currents
– AC currents fluctuate in magnitude and direction, while DC currents remain constant over time.- AC currents are widely used in households and industries due to their ability to be easily converted through transformers.- DC currents are mainly used in applications requiring a steady flow of energy, like batteries and electronic circuits.
Explanation of key terms: RMS Value, Average Value, and Peak Value
– RMS Value: Represents the equivalent DC value of an AC signal, aiding in comparing it to DC circuits.- Average Value: Arithmetic mean of the instantaneous values of an AC wave over one complete cycle.- Peak Value: The maximum value reached by an AC signal above or below its average value.

RMS Value and Average Value in AC
Understanding RMS Value in AC circuits
– The RMS value in AC circuits denotes the equivalent DC value of an AC signal, making it easier to compare with DC circuits.- It is crucial in determining the effective power dissipation in a circuit and is calculated as the square root of the average of the square of the instantaneous values.
Calculating Average Value in AC waveforms
– Average value in AC waveforms represents the arithmetic mean of the instantaneous values over a complete cycle.- It is used in assessing the amount of power delivered by the AC signal over time and can be obtained by integrating the waveform over one full cycle.

Peak Value and Instantaneous Value
Defining Peak Value in AC signals
– The peak value in AC signals refers to the maximum amplitude reached by the waveform during a cycle.- It is essential in determining the maximum voltage or current that the circuit will experience.
Differentiating between Peak Value and Instantaneous Value
– While the peak value represents the highest point of the signal, the instantaneous value is the value at a specific point in time.- Understanding this difference is crucial in analyzing the characteristics and behavior of AC signals accurately.
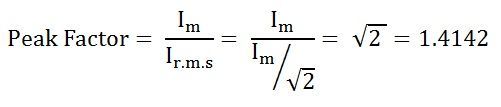
Peak Value and Instantaneous Value
Defining Peak Value in AC signals
– The peak value in AC signals refers to the maximum amplitude reached by the waveform during a cycle.- It is essential in determining the maximum voltage or current that the circuit will experience.
Differentiating between Peak Value and Instantaneous Value
– While the peak value represents the highest point of the signal, the instantaneous value is the value at a specific point in time.- Understanding this difference is crucial in analyzing the characteristics and behavior of AC signals accurately.
Peak Factor and Form Factor
Exploring the significance of Peak Factor in AC signals
– The peak factor in AC signals is the ratio of the peak value to the RMS value.- It helps in understanding the peak amplitude variations in the signal.
Analyzing Form Factor in AC waveforms
– Form factor in AC signals is the ratio of RMS value to the average value.- It provides insights into the waveshape and distribution of energy in the signal.
Relationship between Peak Factor and Form Factor
Understanding how Peak Factor and Form Factor are related in AC circuits
– The relationship between Peak Factor and Form Factor in AC circuits lies in their calculations based on different aspects of the waveform.- While Peak Factor focuses on the peak value compared to the RMS value, Form Factor looks at the RMS value in relation to the average value.
Implications of Peak Factor and Form Factor in analyzing AC waveforms
– Understanding the relationship between Peak Factor and Form Factor is essential for a comprehensive analysis of AC waveforms.- The Peak Factor and Form Factor values provide insights into the characteristics and distribution of energy in the AC signal.