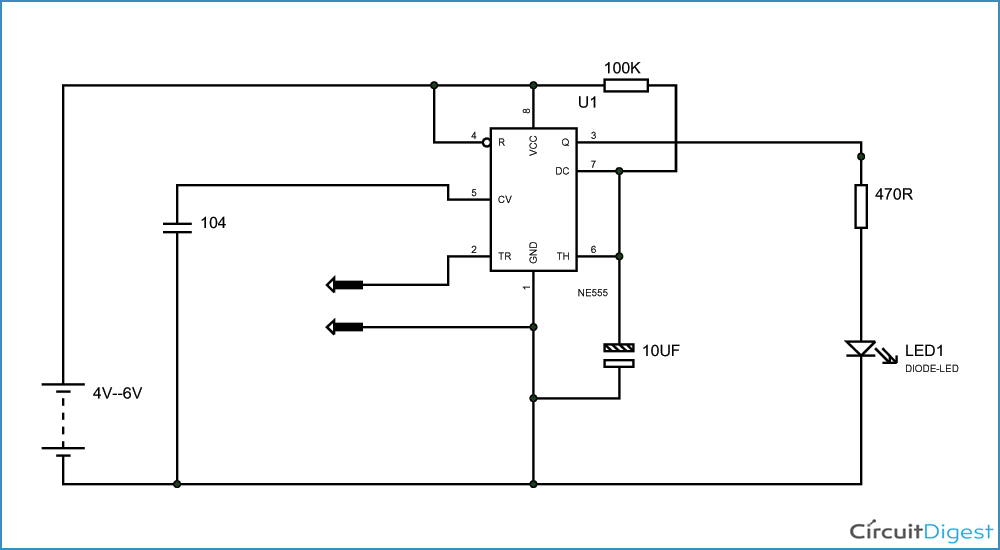
Introduction to Simple Touch Sensitive Switch Circuit
Importance of Touch Sensitive Switch in Electronic Circuits
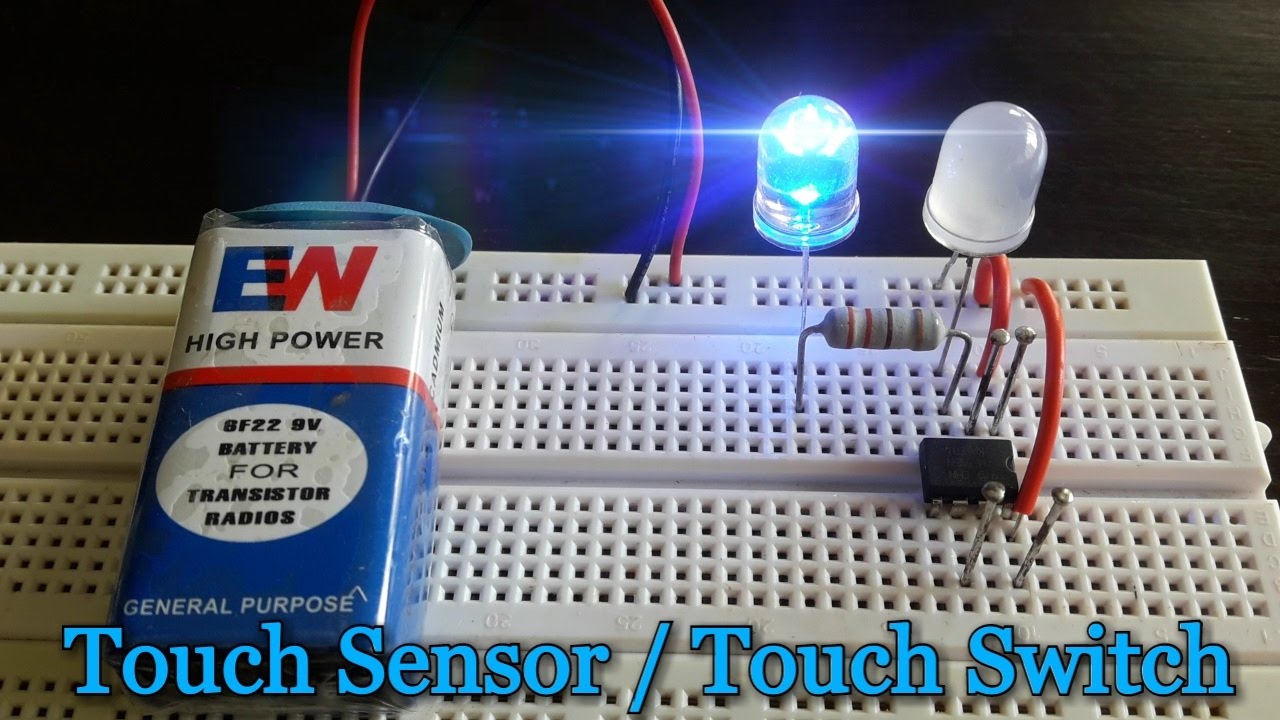
In today's world, the need for touch-sensitive switches has grown significantly due to the convenience they offer in various electronic applications. The Simple Touch Sensitive Switch Circuit using components like the 555 Timer and BC547 Transistor provides an efficient way to control devices with just a touch, eliminating the need for physical buttons or switches.
Overview of Components Required for the Circuit
To create the touch-sensitive switch circuit, you will need the following components:- 555 Timer- BC547 Transistor- Resistors- Capacitors- Touch sensor- Power supply
These components work together to create a circuit that responds to touch inputs, making it ideal for applications where a touch-sensitive interface is preferred.
Understanding the 555 Timer IC
Pin Configuration of 555 Timer IC
In the 555 Timer IC, there are different pins serving specific functions. Pin configuration includes VCC, Trigger, Output, Reset, Control Voltage, Threshold, and Discharge, each playing a crucial role in the circuit's operation.
Operational Modes of 555 Timer IC
The 555 Timer IC functions in various modes like A-Stable, Mono-Stable, and Bi-Stable modes, depending on the circuit configuration. Each mode offers distinct operational characteristics that cater to different electronic applications effectively. Understanding these modes is essential for utilizing the 555 Timer IC efficiently in touch-sensitive switch circuits.

BC547 Transistor in the Circuit
Role of BC547 Transistor in Touch Switch Circuit
The BC547 transistor serves as a crucial component in the touch-sensitive switch circuit. It is used to amplify and switch electronic signals in the circuit, allowing for the detection and response to touch input. The transistor acts as a key element in controlling the flow of current through the circuit based on the touch input received, enabling the switch to operate effectively.
Working Principle of BC547 Transistor
The BC547 transistor operates based on the bipolar junction transistor (BJT) principle. When a small current is applied to the base terminal of the transistor, it allows a larger current to flow between the collector and emitter terminals. This amplification effect is essential in the touch switch circuit, where the transistor amplifies the signal from the touch input, enabling the circuit to activate and perform the desired function efficiently.

Building the Touch Sensitive Switch Circuit
Construction of the Circuit Diagram
The circuit diagram for the touch-sensitive switch involves connecting the BC547 transistor along with the 555 timer. The components are arranged in a way that enables the detection of touch input and triggers the switching action effectively. This construction ensures that the circuit functions reliably in response to touch stimuli.
Connection Setup and Wiring Details
Proper wiring is crucial to the functionality of the touch-sensitive switch circuit. The connections between the resistor, capacitor, transistor, and timer must be correctly established to ensure smooth signal amplification and switching. A systematic setup of the components according to the circuit diagram is essential for the successful operation of the touch-sensitive switch.
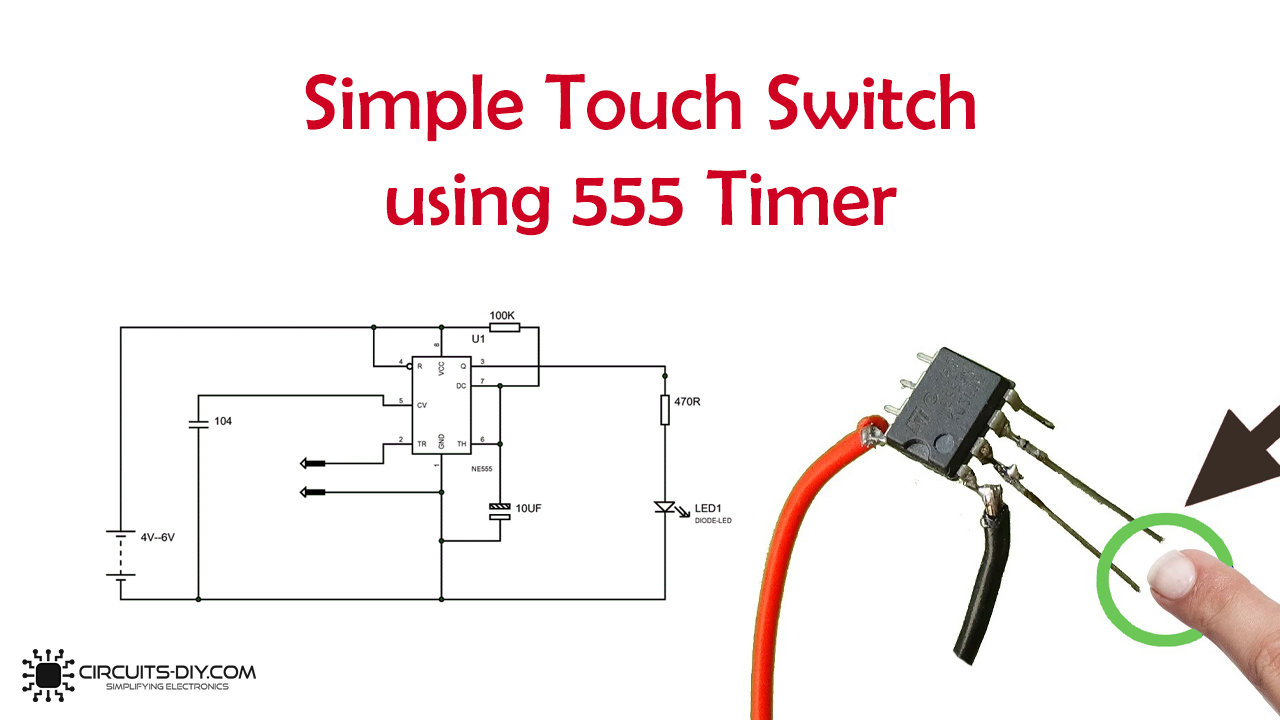
Functioning of the Touch Sensitive Switch Circuit
Discussion on How the Circuit Operates
The touch-sensitive switch circuit operates by utilizing the touch input to trigger the switching action. When a touch is detected, the BC547 transistor amplifies the signal, which in turn affects the 555 timer. This interaction leads to a change in the output state of the circuit, enabling it to act as a switch in response to touch stimuli.
Analysis of the Output from the Circuit
The output from the touch-sensitive switch circuit is a reliable switching mechanism that responds effectively to touch inputs. By analyzing the output signals, it can be observed that the circuit functions efficiently in detecting and translating touch interactions into switching actions. The designed circuit ensures a smooth and consistent response to touch stimuli without the need for physical buttons.