
Introduction
Explanation of Quantization and Sampling
– Quantization in signal processing involves mapping input values to output values from a discrete set of possibilities. This allows for digital representation of analog signals.
- Sampling is the process of converting a continuous signal into a discrete signal by selecting specific points at regular intervals.
Overview of Compression Types and Laws
– Compression in communication systems reduces the size of data for efficient storage and transmission.
-
Different compression types include lossless compression that retains all original data and lossy compression that sacrifices some data for higher compression ratios.
-
Compression laws such as Huffman coding and Run-Length Encoding govern how data is compressed and decompressed.

Understanding Quantization
Definition and Importance of Quantization
Quantization is the process of converting continuous analog signals into discrete digital signals by assigning specific values from a finite set. It is crucial in signal processing for accurately representing analog data in digital systems.
Types of Quantization Techniques
1. **Uniform Quantization**: Divides the range of input values equally into quantization levels.2. **Non-Uniform Quantization**: Assigns different intervals to various parts of the input signal based on perceptual importance.3. **Mid-Tread Quantization**: Sets the midpoint of the quantization interval as the reference point for signal representation.

Significance of Sampling
Explanation of Sampling Process
Sampling is the process of capturing and representing continuous signals as a series of discrete values at specific time intervals. It plays a vital role in converting analog signals into digital formats for processing and transmission.
Laws Governing Sampling Theory
1. **Nyquist-Shannon Sampling Theorem**: States that to accurately reconstruct a signal, the sampling rate must be at least twice the signal's highest frequency component.2. **Nyquist Frequency**: It refers to half of the sampling rate and determines the maximum frequency that can be captured correctly during sampling.
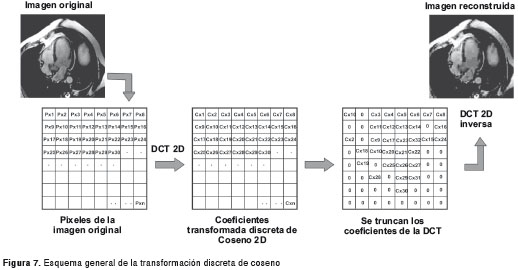
Types of Compression
Lossy Compression Techniques
– Lossy compression techniques reduce file sizes by eliminating unnecessary data or details.- Examples include JPEG for images and MP3 for audio.- This method results in some loss of quality, but offers higher compression ratios.
Lossless Compression Techniques
– Lossless compression ensures that the original data can be reconstructed exactly from the compressed data.- Algorithms like ZIP and FLAC are commonly used for lossless compression.- While the compression ratios are lower compared to lossy techniques, there is no loss of quality in the data.

Lossy Compression Laws
Exploring Lossy Compression Laws
– Lossy compression techniques reduce file sizes by eliminating unnecessary data or details. Examples include JPEG for images and MP3 for audio. This method results in some loss of quality, but offers higher compression ratios.
Effects of Lossy Compression on Data
– Lossy compression can lead to a decrease in data quality due to the elimination of certain details. While it allows for smaller file sizes and efficient storage, there is a trade-off with the loss of some data. This can affect the fidelity of images and audio files, impacting their overall clarity and sharpness.
