
Introduction
Background on the topic of bulb brightness in series and parallel circuits
In the scenario of connecting two bulbs in either series or parallel, determining which bulb will glow brighter can be a point of confusion for many. The brightness of bulbs in series or parallel circuits is influenced by various factors such as voltage, current, and resistance relationships within the circuit.
Importance of understanding power dissipation in light bulbs
Understanding power dissipation in light bulbs is crucial for optimizing performance and efficiency in electrical circuits. By comprehending how the arrangement of bulbs affects brightness, individuals can make informed decisions when designing lighting systems for different applications.

Series Circuit
Explanation of light bulb behavior in a series circuit
In a series circuit, like the one with two bulbs in series, the same current flows through each component. As a result, the 80W bulb, having higher resistance compared to the 100W bulb, will glow brighter due to the relationship between resistance and power dissipation.
Comparison between 80W and 100W bulbs in terms of brightness
The 80W bulb shines brighter in a series circuit as the current passing through both bulbs remains constant, and the 80W bulb's higher resistance allows it to convert more power into light compared to the 100W bulb.

Parallel Circuit
Explanation of light bulb behavior in a parallel circuit
In a parallel circuit, each component receives the full voltage supplied by the source, resulting in different currents passing through the bulbs. In this case, the 100W bulb will glow brighter when connected in parallel with the 80W bulb since it has lower resistance, allowing it to convert more power into light.
Comparison between 80W and 100W bulbs in terms of brightness
In a parallel circuit, the 100W bulb shines brighter as it receives the full voltage, leading to a higher power dissipation and brighter illumination compared to the 80W bulb.
Factors Affecting Brightness
Discussion on power dissipation and resistance in series and parallel circuits
In a parallel circuit, each component receives full voltage, leading to different currents and brightness levels. The 100W bulb illuminates brighter in parallel due to lower resistance, converting more power to light. In series, voltage divides between bulbs, resulting in the 80W bulb glowing dimmer. Resistance plays a crucial role in determining brightness in different circuit configurations.
Impact of power rating on bulb brightness in different circuit configurations
Power rating directly influences bulb brightness in series and parallel arrangements. Higher wattage bulbs illuminate brighter in parallel circuits due to full voltage supply, unlike in series where voltage sharing occurs. Thus, the 100W bulb shines brighter in parallel while the 80W bulb appears dimmer in a series setup.
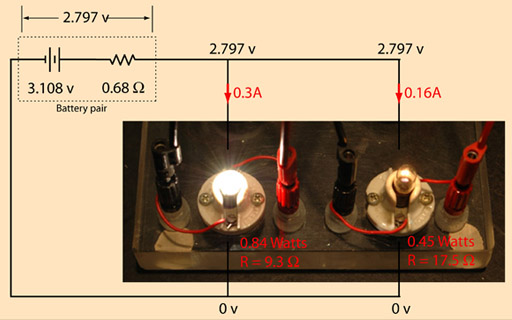
Practical Applications
Real-world examples of series and parallel circuit setups
– Series Circuits: Used in holiday lights to ensure all bulbs share the same current. – Parallel Circuits: Common in homes for independent functioning of multiple light bulbs.
Tips for optimizing bulb brightness based on circuit type
– Select higher wattage bulbs for parallel setups to achieve brighter illumination. – Use series circuits for applications where uniform brightness across all bulbs is desired.