
Cables Feeder Protection
Faults Types, Causes & Differential Protection
In the realm of cables feeder protection, various fault types can occur, leading to disruptions in the system. Common types of faults include electrically induced failures, mechanically induced failures, thermally induced failures, metallic shield damage, and poor metallic shield contact. These faults may arise from lightning strikes, switching surges, partial discharges, or other environmental factors.
Common Types of Faults
- Electrically induced failures
- Mechanically induced failures
- Thermally induced failures
- Metallic (semiconducting) shield damage
- Poor Metallic Shield Contact
Common failure modes:
– Electrically induced failures- Mechanically induced failures- Thermally induced failures
Explanation of each fault
Each fault type poses unique challenges and requires specific protection mechanisms to mitigate them effectively.

Cable Feeder Protection
Differential Protection
In the realm of cable feeder protection, various fault types can occur, leading to disruptions in the system. Common types of faults include electrically induced failures, mechanically induced failures, thermally induced failures, metallic shield damage, and poor metallic shield contact. These faults may arise from lightning strikes, switching surges, partial discharges, or other environmental factors.
Differential Protection (87): Lightning, switching surges, partial discharges
When it comes to cable feeder protection, differential protection plays a crucial role in detecting faults such as those caused by lightning, switching surges, and partial discharges. These types of faults can induce inaccuracies in relays, leading to errors in protection schemes. To effectively address these challenges, specific differential protection mechanisms need to be implemented to ensure the reliability and efficiency of the protection system.

Overcurrent Protection for Cables
Network Configuration: MV distribution networks, Radial Ringed type, Double-end feed with NO point
LV distribution networks and common configurations
In the realm of cable feeder protection, various fault types can occur, leading to disruptions in the system. Common types of faults include electrically induced failures, mechanically induced failures, thermally induced failures, metallic shield damage, and poor metallic shield contact. These faults may arise from lightning strikes, switching surges, partial discharges, or other environmental factors. Differential Protection (87) is crucial in detecting faults caused by lightning, switching surges, and partial discharges. Implementing specific differential protection mechanisms is vital to ensure the reliability and efficiency of the protection system.
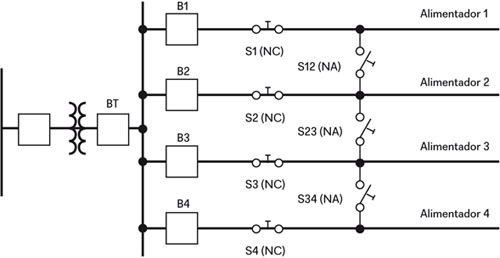
Overcurrent Protection for Cables
Network Configuration: MV distribution networks, Radial Ringed type, Double-end feed with NO point
LV distribution networks and common configurations
In the realm of cable feeder protection, various fault types can occur, leading to disruptions in the system. Common types of faults include electrically induced failures, mechanically induced failures, thermally induced failures, metallic shield damage, and poor metallic shield contact. These faults may arise from lightning strikes, switching surges, partial discharges, or other environmental factors. Differential Protection (87) is crucial in detecting faults caused by lightning, switching surges, and partial discharges. Implementing specific differential protection mechanisms is vital to ensure the reliability and efficiency of the protection system.

Section 6: Transformer Protection
Further discussion on Differential Protection
In the domain of cable feeder protection, various fault types can emerge, causing disruptions in the system. Common types encompass electrically induced failures, mechanically induced failures, thermally induced failures, metallic shield damage, and poor metallic shield contact. These faults, stemming from lightning strikes, switching surges, partial discharges, or other environmental factors, highlight the importance of Differential Protection (87). This protection mechanism is crucial in detecting faults caused by lightning, surges, and discharges, ensuring the reliability and efficiency of the protection system. Implementing specific differential protection mechanisms is imperative to safeguard the integrity of the system.