
Introduction to Three-Phase Induction Motors
Basic overview of three-phase induction motors
Three-phase induction motors are widely used in various industrial applications due to their reliability and efficiency. They operate based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a rotating magnetic field is created within the stator to induce currents in the rotor, resulting in motion. These motors do not require any external excitation and are self-starting, making them simple and cost-effective for a range of applications.
Importance and applications of three-phase induction motors
Three-phase induction motors are crucial in powering equipment such as pumps, compressors, fans, and conveyors across industries like manufacturing, agriculture, and construction. Their ability to provide constant speed and torque, along with their rugged design, makes them ideal for continuous operation in various challenging environments. These motors play a vital role in driving industrial processes efficiently and reliably.
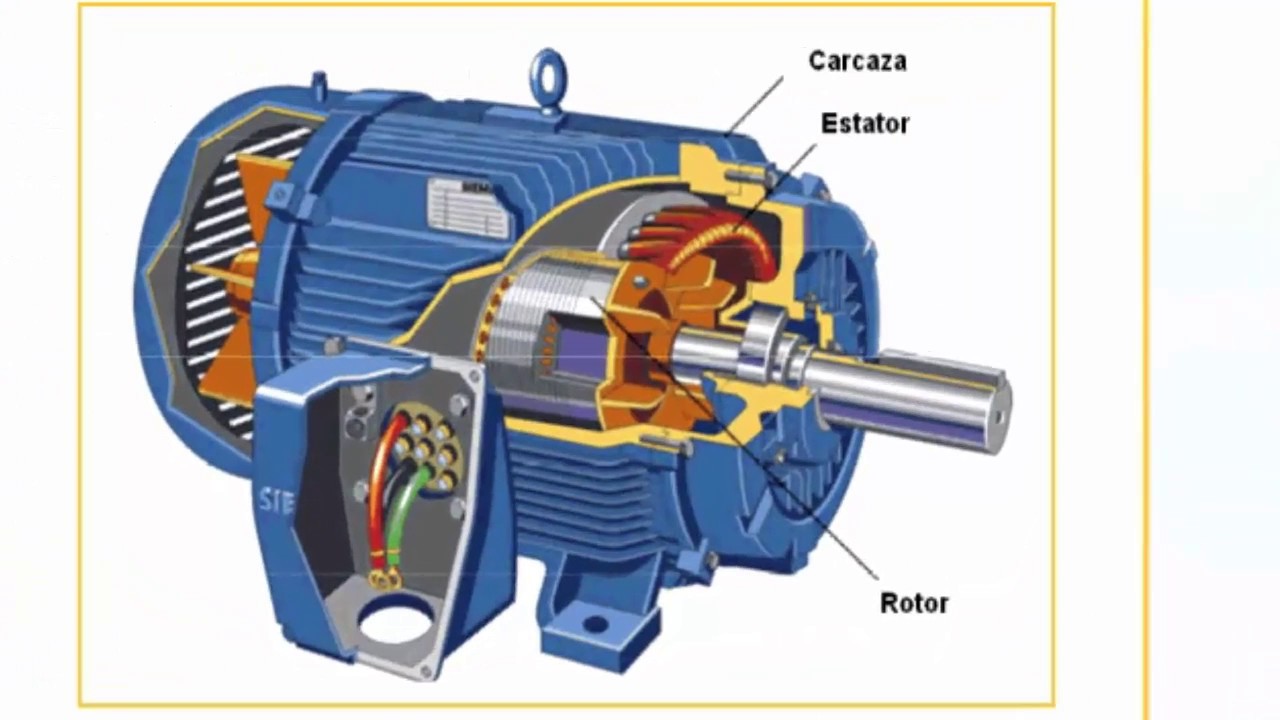
Working Principle of Three-Phase Induction Motors
Explanation of the working principle
Three-phase induction motors operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, generating a rotating magnetic field in the stator to induce motion in the rotor without the need for external excitation. This design enables reliable and efficient performance in a wide range of industrial applications. The rotor's movement in response to the rotating magnetic field allows these motors to deliver constant speed and torque output for various tasks.
Differences between single-phase and three-phase motors
**Single-Phase Motors** | **Three-Phase Motors**— | —Typically used in domestic applications | Commonly found in industrial settingsRequire a starting mechanism | Self-startingLess efficient compared to three-phase motors | More efficient and offer better power outputLimited in power capacity | Suitable for high-power applicationsLess expensive | Higher initial cost, but cost-effective in the long run

Types of Three-Phase Induction Motors
Overview of various types of three-phase induction motors
Three-phase induction motors come in various types including squirrel cage, wound rotor, and double squirrel cage motors. Each type has specific design features and applications that make them suitable for different industrial needs.
Advantages and disadvantages of each type
**Squirrel Cage Motors** | **Wound Rotor Motors** | **Double Squirrel Cage Motors**— | — | —Simple in design, low maintenance | High starting torque, adjustable speed | Increased efficiency, suitable for high inertia loadsNot suitable for variable speed applications | Require regular maintenance of slip rings | Higher initial cost, complex constructionCost-effective, widely used | Greater control over speed and torque | Improved performance at low speeds
These various types offer different performance characteristics, catering to a range of industrial requirements.

Factors to Consider When Selecting Three-Phase Induction Motors
Key considerations for selecting the right motor
When choosing a three-phase induction motor, factors such as the specific application, required power rating, efficiency levels, and the operating environment play a crucial role. **Efficiency, power rating, and operating environment** are critical aspects to evaluate to ensure optimal motor performance and longevity.
Efficiency, power rating, and operating environment
**Efficiency** of the motor directly impacts energy consumption, with higher efficiency models offering cost savings in the long run. **Power rating** must align with the operational requirements to prevent overload or inefficiencies. Additionally, considering the **operating environment** helps in selecting a motor that can withstand conditions like temperature variations and dust levels.

Starting and Control Methods for Three-Phase Induction Motors
Various methods for starting the motor
When addressing the start-up of three-phase induction motors, different methods can be employed, including direct-on-line (DOL) starting, star-delta starting, and soft starters. **DOL starting** involves directly connecting the motor to the power supply, suited for smaller applications. **Star-delta starting** reduces the starting current by initially connecting the motor winding in star configuration and then switching to delta. **Soft starters** provide a gradual increase in voltage during start-up, reducing mechanical stress and electrical disturbances.
Control techniques for speed and torque regulation
Controlling the speed and torque of three-phase induction motors can be achieved through methods like variable frequency drives (VFDs) and slip ring rotors. **VFDs** allow for precise control over motor speed by adjusting the frequency of the electrical supply. Alternatively, motors equipped with **slip ring rotors** enable external resistors to be added to the circuit, altering torque characteristics. These control techniques enhance operational efficiency and facilitate customization based on specific application requirements.