
Real Ground vs. Virtual Ground Explained
Difference Between Real Ground and Virtual Ground
Real ground is established when a terminal is physically connected to the ground or earth. On the other hand,
Real Ground: Physical connection to the earth
Real ground signifies the direct physical connection of a terminal to the actual ground or earth, ensuring a zero potential reference point.
Virtual Ground: Concept in Op-Amps assuming ground potential
Virtual ground, commonly utilized in operational amplifiers (Op-Amps), is a theoretical node that is considered to have the same potential as the ground terminal, despite not being physically connected to the ground. It provides a reference point for circuit operations without requiring an actual physical connection to the ground.

Virtual Ground Concept in Op-Amps
Conditions for Virtual Ground Existence
– Same voltages at both terminals- Terminals should not act as ground
Applicability in Negative Feedback Op-Amps
– Suitable for Negative Feedback Configuration- Used in inverting and non-inverting amplifiers, voltage follower, etc.
Inapplicability in Positive Feedback Configurations
– Not applicable in Positive Feedback setups like Schmitt trigger- Virtual ground concept relies on Negative Feedback arrangement in Op-AmpsVirtual Ground implies a theoretical connection point with ground potential, vital for several operational amplifier setups. It allows for circuit operations to reference a common point without actual physical grounding. This concept thrives under specific conditions, primarily in Negative Feedback systems, excluding Positive Feedback arrangements such as Schmitt triggers.
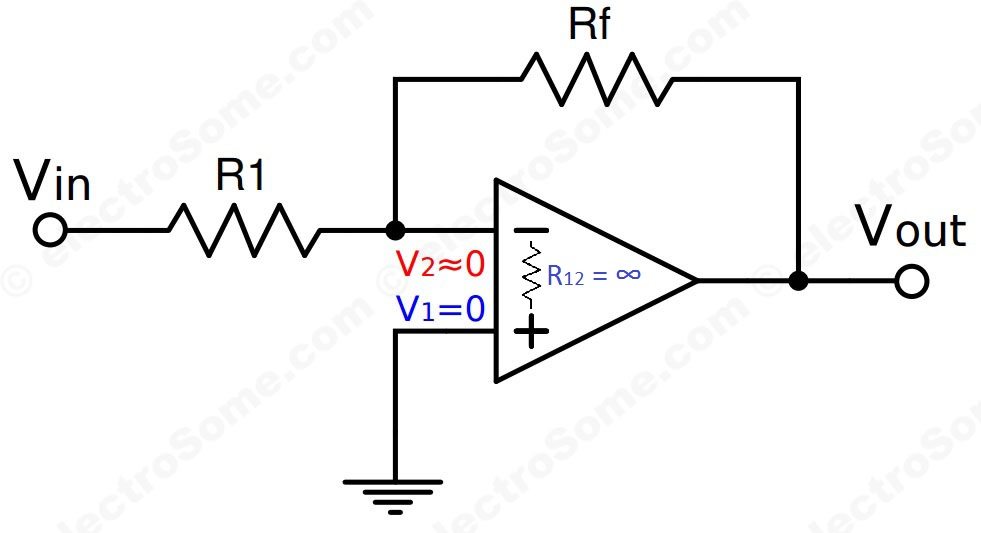
Virtual Ground Applications
Virtual Ground in Inverting Amplifiers
– In inverting amplifier configurations, the virtual ground concept plays a crucial role.- It ensures that the input signal is referenced to the virtual ground point, facilitating the amplification process.
Virtual Ground in Non-Inverting Amplifiers
– Similarly, in non-inverting amplifier setups, virtual ground is utilized to provide a reference point for the input signal.- This allows for accurate amplification while maintaining the desired phase relationship between input and output signals.
Virtual ground serves as a theoretical connection point with ground potential in operational amplifier circuits. By adhering to specific conditions, particularly in Negative Feedback systems, virtual ground enables efficient circuit operations without the need for physical grounding. Its applications are prevalent in various amplifier configurations, enhancing the performance and functionality of electronic circuits.

Blog Section:
Characteristics of Real Ground
Properties of Real Ground Connection
– Real ground involves a physical connection to the earth or ground terminal.- It provides a zero voltage reference point for electrical circuits.- Ensures safety by diverting excess current to the ground.
Functionality of Real Ground in Electrical Circuits
– Real ground helps in stabilizing voltage levels within the circuit.- It prevents electrical noise and interference.- Facilitates effective grounding in power systems, ensuring equipment safety.
In electrical and electronic systems, real ground serves as a vital component for proper functioning and safety. Its physical connection to the earth provides stability, reference point, and safety measures crucial for various applications. By ensuring a secure path for excess current and stable voltage levels, real ground enhances the reliability and performance of electrical circuits.
